Nearly half of online registrations now flagged as attacks, says identity report
Nearly 50% of online registrations in 2024 were flagged as attacks, according to a new customer identity report by Auth0.

A new report from Auth0 has found that nearly half of all customer registration attempts in 2024 were identified as potential attacks, signalling a growing threat to online identity systems. According to the Customer Identity Trends Report 2025, 46% of sign-up requests processed through the Auth0 platform met attack criteria.
Table Of Content
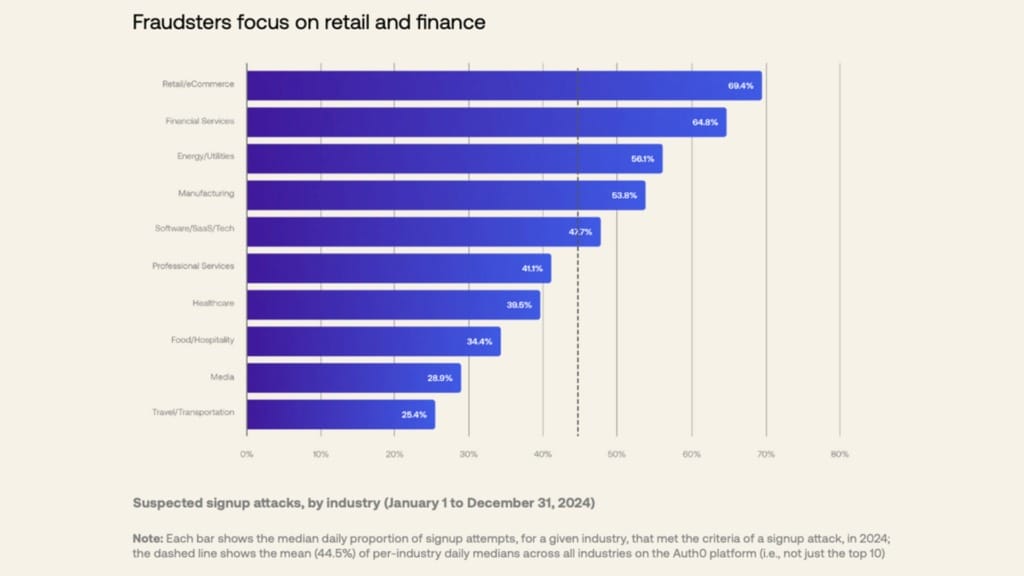
The report outlines how attackers increasingly view login pages as entry points to sensitive information and customer benefits. In one case, a prolonged attack on the retail and e-commerce sector saw fake sign-ups surpass genuine ones by a ratio of 120 to one. The financial and professional services sectors were also frequent targets, given the nature of the personal and financial data they hold.
These findings underscore the vulnerability of digital sign-up systems and highlight the ongoing risks organisations face in protecting customer data and preserving trust.
User experience decisions shaped by trust and security
Trust and security have become key factors in a customer’s decision to register or sign in to a digital service. The report reveals that 74% of users prioritise a company’s reputation and trustworthiness when deciding to create an account, while 72% value security above all else. Product quality and price take a back seat in the initial stages of customer engagement.
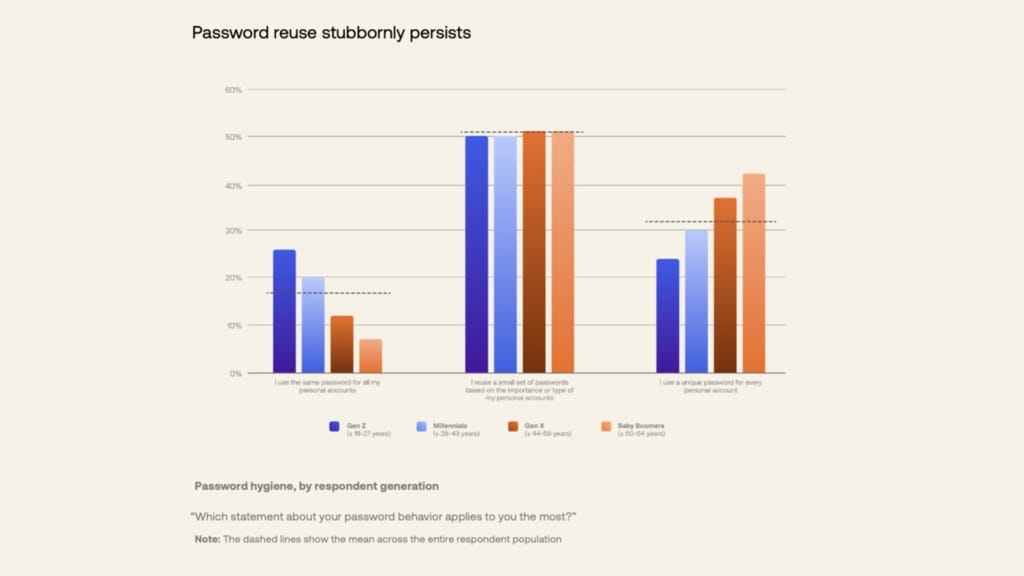
Despite this, poor login practices persist. The survey found that 68% of users admitted to reusing passwords across multiple accounts, significantly increasing the risk of breaches. This issue is compounded by user frustration—62% of respondents said long login forms are a source of irritation, and 25% have abandoned purchases due to sign-up or login issues. The impact is particularly notable among Gen Z and Millennial users, who are more sensitive to digital friction.
However, alternative authentication methods are gaining acceptance. Passkeys are increasingly seen as convenient by younger users, and biometric options such as fingerprint or facial recognition are considered the most secure by a majority of respondents. These trends point to a demand for login solutions that are both seamless and secure.
AI trust deficit continues despite growing adoption
While companies continue to introduce AI-powered tools to improve digital services, customer trust in these agents remains low. The report found that 70% of users still prefer interacting with human agents. Among those unwilling to engage with AI, 44% cited a lack of trust in how these systems handle personal data. More broadly, 60% expressed concern about the effect of AI on the privacy and security of their digital identities.
The risks extend beyond perception. Many organisations are deploying AI tools without proper identity and access management controls. This opens the door to unauthorised access, data leakage, and unintended actions performed by AI systems. To address these vulnerabilities, companies are encouraged to adopt safeguards such as authentication, secure API calls, user confirmation, and fine-grained authorisation.
As AI becomes more embedded in customer service and online experiences, the need for built-in trust mechanisms has never been more critical.
Closing the gap through transparency and oversight
Despite current scepticism, many users are open to using AI—under the right conditions. According to the report, 38% of respondents said they would be more willing to trust AI agents if their actions were reviewed or approved by humans. Transparency, ethical standards, and clearly defined responsibilities also play a vital role in building trust.
The report concludes that security is no longer the sole concern of IT departments. Instead, it is a shared responsibility that cuts across departments—from product development to customer experience. To maintain trust and benefit from AI’s potential, businesses must ensure strong identity management practices and clearly communicate how they protect users and data.
The report reinforces a clear message: building digital trust requires a secure, user-friendly experience and responsible AI deployment.
















